Autores
dos Santos Filho, J.M. (UFPE) ; Pinheiro, S.M. (UFPB) ; Gomes da Silva, M. (UFPE) ; Siqueira Silva, L.V. (UFPE) ; Militão, G.C.G. (UFPE) ; Norberto da Silva, P.B. (UFPE)
Resumo
Natural products and their derivatives are important sources for drug discovery,
including their structural modification by molecular hybridization. Amino acids
(AA) have a wide range of biological activities and their association with
pharmacophoric scaffolds is expected to improve the performance of these new
products and minimize their adverse effects. Therefore, the structural
modification strategy of glycine (Gly) and phenylalanine (Phe) provides a
theoretical basis for the discovery of antitumor compounds. The thiosemicarbazides
arising from this strategy exhibit great potential in medicinal chemistry.
Palavras chaves
DNP-amino acids; Thiosemicarbazides; Anticancer activity
Introdução
The molecular modification of amino acids (AA) by hybridizing them with
pharmacophoric groups or other natural products are an important strategy for
the discovery of new molecules exhibiting a plethora of biological responses,
e.g., antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic, and especially
anticancer activity [XU et al, 2021]. The chosen strategy for this work
has envisaged the design of derivatives bearing the thiosemicarbazide moiety due
to its importance in medicinal chemistry [ACHARYA et al, 2021], starting
from glycine (Gly) and phenylalanine (Phe) as structural backbones. Two series
of thiosemicarbazides, DNP-Gly(1-13) and DNP-Phe(1-13), were designed,
synthesized and undergone anticancer studies against the cell lines HEP-2
(cervix adenocarcinoma) and MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma). The preliminary
results have pointed to good outcomes and the nature of the selected
substituents gives clues on the structure-activity relationship (SAR) observed
for the 26 unpublished compounds. A part of the molecular modification developed
in this work was the introduction of a 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) ring linked to
the α-nitrogen, an important contribution to the biological responses [NEPALI
et al, 2019].
Material e métodos
Compounds DNP-Gly(1-13) and DNP-Phe(1-13) were tested for their cytotoxicity
against cancer cell lines HEP-2 (cervix adenocarcinoma) and MCF-7 (breast
adenocarcinoma). The 3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium
bromide (MTT, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) reduction assay was
used after 72 h incubation. For all experiments, cells were plated in 96-well
plates (105 cells/mL for adherent cells or 3×105 cells/mL for leukemia
and 106 for PBMC). After 24 h the compounds were diluted (50 µM) in a medium
with 0.5% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO, Vetec, Brazil) and tumor cells were screened
in triplicate at three different experiments. To determine the concentration
that causes 50% of inhibition (IC50) cells were treated with
concentrations ranging from 0.3 to 50 µM. Negative control received the same
amount of DMSO. Doxorubicin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) (0.01–5 µg/mL) was
used as the positive control. After 69 h of treatment, 20 µL of MTT (5 mg/mL;
Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) was added. At the end of the incubation, the MTT
formazan product was dissolved in 100 μL of DMSO and the absorbance was measured
at 570 nm in a plate spectrophotometer (Varioskan Flash; Thermo Scientific,
Finland). The percentage of cell growth inhibition (mean and standard
deviation) after treatment with compounds at a single concentration of 50 µM was
calculated. Only compounds that presented at least 75% of growth inhibition at
three cell lines were considered active for determining the IC50
values. The IC50 values were calculated by nonlinear regression with
a confidence interval of 95%.
Resultado e discussão
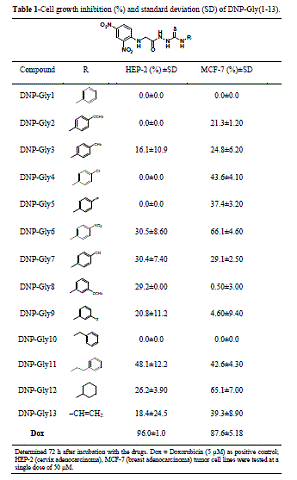
According to the results disclosed in Table 1, the series DNP-Gly(1-13) have
exhibited poor anticancer activities. In comparison to the standard drug
doxorubicin, almost all responses against HEP-2 and MCF-7 were under 50%,
indicating inactivity. DNP-Gly12 has presented the best cell growth inhibition for
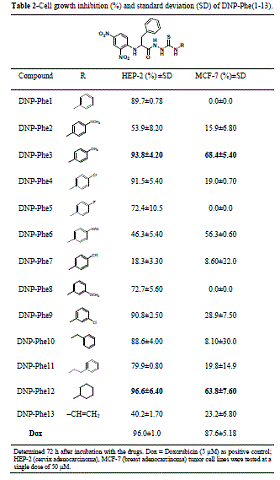
MCF-7 with a value of 65.1%. By analyzing the data in Table 2, an impressive
improvement in the biological outcomes was observed for the series DNP-Phe(1-13)
They have exhibited good to excellent inhibition activities, with evidence that
electronic properties also can modulate the results. The introduction of the
CH2Ph group at the α-carbon of the starting AA substrate entails an
important modification of the lipophilicity of all compounds under study, which
could be considered as the determining physicochemistry property affecting the
cytotoxic responses for the thiosemicarbazides built from the phenylalanine
backbone. Outstanding results were found for compound DNP-Phe3, with cell growth
inhibition of 93.8% for HEP-2 and 68.4% for MCF-7, while the most active
thiosemicarbazide was the derivative DNP-Phe12 with inhibition values of 96,6% and
63.8% for HEP-2 and MCF-7 respectively. The comparison between both series
suggests that it is possible to improve the anticancer activity of the DNP-AA
derivatives by modulating their structures either by changing the AA scaffold or
by modifying the pharmacophore attached to the structure.
Conclusões
After synthesizing the two thiosemicarbazide series DNP-Gly(1013) and DNP-Phe(1-
13), designed as potential anticancer compounds, this hypothesis was confirmed by
the outcomes found for the tumor cell growth inhibition of the compounds DNP-
Phe(1-13), with special attention to derivatives DNP-Phe3 and DNP-Phe12, whose
inhibition of the HEP-2 cell line was 93.8% and 96.6% respectively. This
investigation suggests that lipophilicity is probably a decisive factor in
anticancer activity. In face of these results, it is possible to deduce that the
proposed molecular modification strategy applied to AA can be quite a success for
the discovery of new drugs.
Agradecimentos
The authors are grateful to FACEPE (Fundação de Amparo a Ciência e Tecnologia do
Estado de Pernambuco) for funding the investigation.
Referências
ACHARYA, P.T., BHAVSAR, Z.A., JETHAVA, D.J., PATEL, D.B., PATEL, H.D. A review on development of bio-active thiosemicarbazide derivatives: Recent advances, J. Mol. Struct. 1226 (2021) 129268.
NEPALI, K., LEE, H.-Y., LIOU, J.-P., Nitro-Group-Containing Drugs, J. Med. Chem. 62 (2019) 2851-2893.
Xu, Q., Deng, H., Li, X., Quan, Z.-S. Application of Amino Acids in the
Structural Modification of Natural Products: A Review Front. Chem. 9 (2021) 650569.
















