Autores
Fajardo, J.R.D. (UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL FLUMINENSE) ; Lessa, M.D. (UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL FLUMINENSE) ; Carneiro, J.W.M. (UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL FLUMINENSE)
Resumo
Structural effects of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) were investigated by the DFT
approach to help rationalize organocatalysis in the formation of polyesters. Based
on previous studies, the selected route involves the NHC acting as a Brønsted base
and activating an alcohol used as a co-initiator. According to previous proposal,
the first step of the reaction occurs with proton abstraction by the NHC, concert
with the attack of the alcohol on the monomer, in the rate-determining step of the
reaction. In the present study we confirm this hypothesis. For the set of NHC we
studied here, there is a clear correlation between the proton affinity of the NHCs
and the activation enthalpy for the first step of the reaction.
Palavras chaves
Lactone; Organocatalysis; DFT
Introdução
Plastic has been present in urban life since the beginning of the 20th century.
Those synthesized from fossil materials will persist in the environment for at
least another 2 centuries. (PORTA 2021) An alternative to sources that produce
persistent materials is the use of biodegradable materials as monomers to form
polymers. Thus, lactones, in a reaction catalyzed by N-Heterocyclic carbenes
(NHC), have been proposed as row material in the formation of aliphatic
polyesters. (DINIZ et al 2021)
Material e métodos
To perform a theoretical analysis of the effects of NHCs structures when applied
as organocatalysts in ring opening polymerization (ROP) reactions of lactones, 24
NHCs shown in Figure 1 were selected. The stationary points of the ROP induced by
the deprotonation of a co-initiator, figure 1, were calculated applying the N12SX
functional and the 6-311+G(d,p) basis set, using ethanol as co-initiator. All
simulations were carried out considering the implicit solvent ethanol, using the
IEFPCM model. The δ-valerolactone was used as a lactone prototype. The
computational method was evaluated in previous works by the group (DINIZ et al
2021), as well as the mechanism selected in the present study.
Resultado e discussão
In a previous work, the ROP route with deprotonation of the co-initiator was
evaluated, where it was proposed that the first step of the reaction is the
rate-determining step. When analyzed against a set of 24 NHCs, with varied
structures, it was observed that the activation energy for this first step
presents a high correlation with the electronic properties of the NHCs. The data
for the selected NHCs are consistent with the mechanism that was proposed
before.
Figure 2 shows that for the first activation enthalpy, compounds of higher
basicity present lower values for this parameter (Figure 2, in green), while
NHCs with lower pKa present higher enthalpy barriers (Figure 2, in
red). The correspondence between the pKa of the NHCs and the
∆H‡ for the TS1 is reflected in a R squared of 0.86,
indicating high
statistical significance.
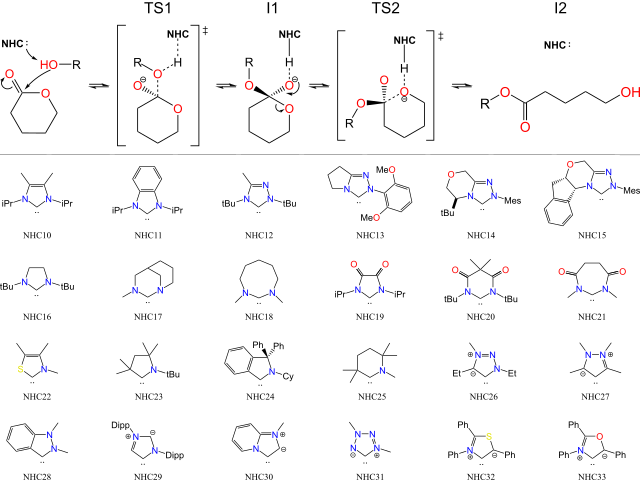
Reaction mechanism studied for the ROP of δ-valerolactone undergoing deprotonation of alcohol, ethanol, and below the 24 selected NHCs
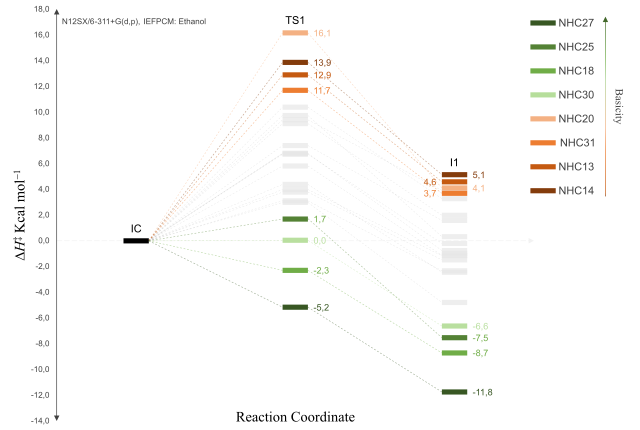
Enthalpy changes (Kcal mol[sup]-1[/sup]) by reaction coordinate, emphasis on the first reaction step and NHCs with lower or higher basicities.
Conclusões
The present data show that the NHCs with structure containing electron donating
groups in the NHC ring are those that lead to the most stable intermediates,
whereas the NHCs containing groups that shift the electron density from the
carbene ring, are those that lead to the less stable intermediates. This
reinforces previous conclusions of our group (DINIZ et al 2021), where electronic
effects, arising from the heteroatoms in the ring and the structural diversity
among the NHCs govern the reaction. Meanwhile, it can be observed that steric
effects have low impact on the reaction kinetics.
Agradecimentos
The authors thank CNPq, FAPERJ and CAPES for the financial support to the work and
the laboratory.
Referências
DINIZ, M. L. et al. A DFT study on the mechanism for polymerization of δ-valerolactone initiated by N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) catalysts. [b]Molecular Catalysis[/b], v. 515, p. 111896, 2021.
PORTA, R. Anthropocene, the plastic age and future perspectives. [b]FEBS Open Bio[/b], v. 11, n. 4, p. 948-953, 2021.
















